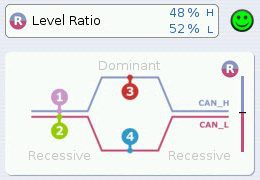
Cable lengths, stub and drop lines
| baud rate | max. trunk line length | max. drop line lenght | max. lenght of all drop lines | max. drop line lenght at multiport tap | max. lenght of trunklines with multiport tap (without droplines) |
| 50 kbit/s | 1000 m | 50 m | 250 m | - | - |
| 125 kbit/s | 500 m | 20 m | 100 m | 4,8 m | 310 m |
| 250 kbit/s | 250 m | 10 m | 50 m | 2,4 m | 120 m |
| 500 kbit/s | 100 m | 5 m | 25 m | 1,2 m | 66 m |
| 1 Mbit/s | 20 m | 1 m | 5 m | 0,3 m | 13 m |
The same length restrictions apply in the CAN FD network. The information in the table here refers to the arbitration baud rate.